Ectopic pregnancy
-
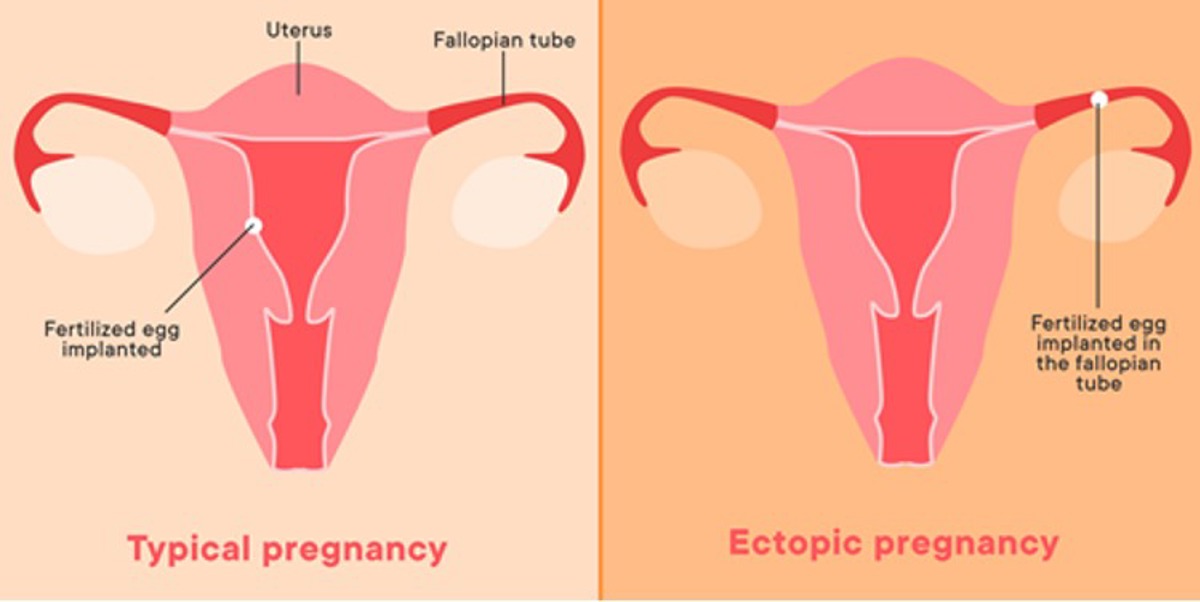
Ectopic pregnancy is when a pregnancy grows outside of the uterus. It can be dangerous.
Ectopic pregnancy most commonly occurs in the fallopian tubes — but it can also happen in other parts of the pelvis. It occurs in about 1 out of 100 pregnancies.
Ectopic pregnancy can be dangerous. It’s possible for an ectopic pregnancy to rupture — causing life-threatening internal bleeding.
-
-
-
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
-
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Pain in your lower tummy — sometimes only on one side of your belly
- Vaginal bleeding — can be heavy or light bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting, or loose bowel motions — sloppy poos
Later symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can include:
- Shoulder tip pain
- Dizzyness
- Feeling faint or lightheaded
Sometimes, ectopic pregnancy has no symptoms.
-
-
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
-
An ectopic pregnancy can be diagnosed by examination, ultrasound scan, and blood tests. It can be difficult to rule out ectopic pregnancy in very early pregnancy, especially if the pregnancy cannot be seen on a scan yet. In this case your healthcare provider will organise for another scan and blood tests to keep an eye on the situation.
If your healthcare provider suspects an ectopic pregnancy, but it's too early to tell, you need to look out for warning signs like: bad pain, heavy bleeding, feeling faint or dizzy, or shoulder tip pain. If you have any of these signs you should go straight to hospital.
-
-
How is an ectopic pregnancy treated?
-
Ectopic pregnancy can be treated with medication or surgery.
For details and advice about ectopic pregnancy, read more on the Healthify He Puna Waiora website.
-
-
-
Do you need urgent help?
If you require urgent medical advice, call Healthline for free on 0800 611 116 anytime or get help from an after hours medical centre or emergency services.